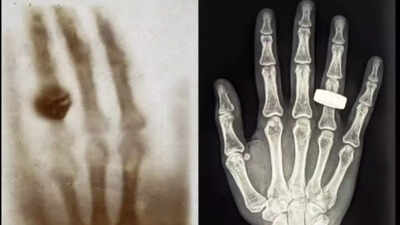
In 1895, a German professor at Physics, Wilhelm Rantjin, was experimenting with the cathode rays while he was stumbling with an accidental discovery that would replace the medical science field. While experimented, he saw a strange brightness in his laboratory in the Flourist screen. This resulted in a new type of radiation identified, which he called “X -ray” because of his unknown role. Recognizing the medical use of this technology, Rantjin quickly took the human body’s first X -ray image. The legendary picture was from his wife’s hand, who was wearing a ring, the beginning of a new era in diagnostic medicine.
Space X Frame 2 Mission gains historic X -ray imaging milestone in space
After more than 130 years when Rantjan made his progress, Space X Frame 2 Missions The staff reproduced their classic X -ray photo, but in space, this time. The Frame 2 Missions boarded a ship carrying four astronauts on a historic journey on March 31, 2025. The purpose of the frame 2 mission was to initially light the first polar orbit human space. With the help of Maltese Cryptoconnery Ticone Chun Wang, the campaign also included three of his colleagues who were with him in the polar campaigns.
It took three and a half days in the frame 2 mission, during which 22 research tests were conducted by the staff. These tests were different from looking at the earth’s poles and doing biological research, such as cultivating mushrooms, up to a more scientific achievement, such as creating images of the human body’s X -ray in space. The first X -ray image taken by the staff was one hand, which was like Rantjan’s first image, but this time it was taken in special conditions. This test was the first time that X -ray imaging was employed on the human body while in space.
Frame 2 staff increases X -ray imaging in space
After successfully image of the X -ray, the Frame 2 staff pushed forward to further the possibility of this technology. The staff moved its diagnostic imaging to the X -ray of the hand, taking other parts of the body, such as arm, pelvic, stomach and chest X -ray. The staff also applied the X -ray technology to diagnose human health imaging, in addition to human health imaging, to diagnose its spacecraft.
In addition, the staff clarified the functionality of the DXA (dual energy X -ray absorption), a type of special X -ray imaging that maintains the amount of bone density, as another field of technical success for the mission.
Frame 2 staff returned to the ground for after -flying
Upon returning from a successful mission, Frame 2 staff’s Space X dragon capsule flexibility landed on April 4, 2025, in the Pacific Pacific, California. The astronauts were recovered by the Space X -Dragon Recovery Ship Shannon and was taken to the Johnson Space Center in NASA in Houston. He started the post -flight study in the form of biometric tests and experiments, which aims to understand how the microority is imposed on the human body.
With the early work of the Frame 2 mission, the integration of space exploration and medical technology has been taken to an extraordinary level, which proves the promise of future studies and applications outside the planet.
Also read | What is the bodies of astronauts in space? Discover the unexpected side effects of living in space